Overview
What Is Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)?
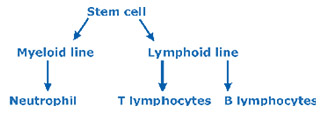
Acute myeloid leukemia, known as AML, occurs when too many neutrophils develop from immature cells of the myeloid line. As the cells decline. AML is less common in children than ALL.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
The following are the most common symptoms of acute myelogenous leukemia. However, each individual may experience symptoms differently.
Symptoms may include:
• Anemia (too few red blood cells)
• Bleeding
• Bruising
• Fever and recurring infections
• Persistent weakness
• Fatigue
• Aches in bones and joints
• Swollen gums, lymph nodes, liver, or spleen
• Weight loss
• Night sweats
The symptoms of acute myelogenous leukemia may resemble other blood disorders or medical problems. Always consult your doctor for a diagnosis.
Causes
Risk Factors for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer. People who think they may be at risk should discuss this with their doctor.
Most cases of AML seem to have no apparent cause.
Possible risk factors include:
• Exposure to radiation, chemicals, and drugs
• A sibling with leukemia
• Having a certain genetic disorder, such as Down's syndrome
• Having a history of a blood disorder such as myelodysplastic syndrome
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML)
You may undergo a number of procedures to determine whether or not you have AML. These include:
• Blood Test
• Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy
• Immunophenotyping
• Cytogenetic analysis
• Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
Additional blood tests and other evaluation procedures may also be performed.
Treatments
Treatment for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Specific treatment for acute myeloid leukemia will be determined by your doctor based on:
• Your age, overall health, and medical history
• The subtype of AML
• Extent of the disease
• Your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies
• Expectations for the course of the disease
• Your opinion or preference
You may have just one type of treatment or a combination. Different types of treatment have different goals. Here are some of the types of treatment and their goals for adults who have AML.
• What treatment may include
• Chemotherapy
The use of anticancer drugs to shrink or kill cancerous cells and reduce cancer spreading to other parts of the body.
• Radiation therapy
The use of high-energy radiation to kill or shrink cancer cells, tumors, and non-cancerous diseases.
• Blood and bone marrow transplant
A specialized therapy to transfer healthy bone marrow cells into a patient after their own unhealthy bone marrow has been eliminated.
(The content above extract from stanfordhealthcare.org)
-
-
Diseases ·
-













 京公网安备13108202000843号
京公网安备13108202000843号